11.2 Cloud Agnostic vs Cloud Native vs Cloud Services
Note
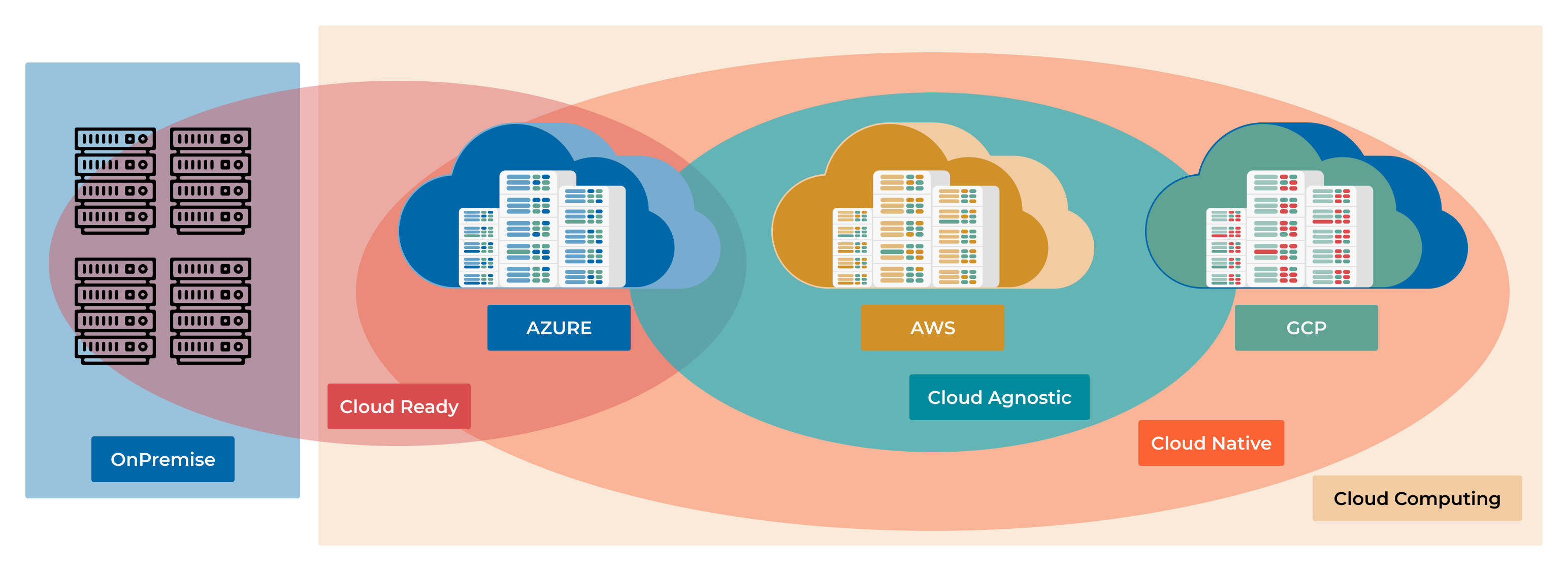
As many things in the IT world, the cloud computing world is full of buzzwords and terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have different meanings. In this section we will clarify the differences between cloud agnostic, cloud native and cloud services.
Cloud Computing
Note
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Cloud Services
Note
Cloud services are any service made available to users on demand via the Internet from a cloud computing provider’s servers as opposed to being provided from a company’s own on-premises servers. Cloud services are designed to provide easy, scalable access to applications, resources and services, and are fully managed by a cloud services provider.
Cloud services include anything from compute, network, storage and database services to full applications and development platforms.
Some examples of cloud services include:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Function as a Service (FaaS)
Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Container as a Service (CaaS)
Database as a Service (DBaaS)
Monitoring as a Service (MaaS)
Security as a Service (SECaaS)
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
API as a Service (APIaaS)
Everything as a Service (XaaS)
Cloud Native
Note
Cloud native is a term that refers to applications that are container-based, dynamically orchestrated and microservices-oriented. Cloud-native technologies are used to develop applications built with services packaged in containers, deployed as microservices and managed on elastic infrastructure through agile DevOps processes and continuous delivery workflows.
In a nutshell, cloud-native is about how applications are created and deployed, not where they are deployed. Cloud-native applications are designed to take full advantage of cloud computing delivery models as well as the agility and flexibility that comes with them. Kubernetes is a the most used cloud-native technology.
Cloud native has the following characteristics:
Application Architecture - Microservices
Deployment solution - Containers and Orchestration
Development process - CI/CD and DevOps
Cloud Agnostic
Note
Cloud agnostic is a term that refers to a software tool or service that is designed to function in any vendor’s cloud computing environment. A cloud-agnostic approach to technology can be beneficial to businesses because it allows them to avoid vendor lock-in, which can occur when a company builds internal workflows or adopts third-party tools that are designed to function optimally with a single cloud provider’s services.
Virtual machines, containers, and Kubernetes are examples of cloud-agnostic technologies. These technologies can be deployed in any cloud environment, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others.