7.1 Getting started
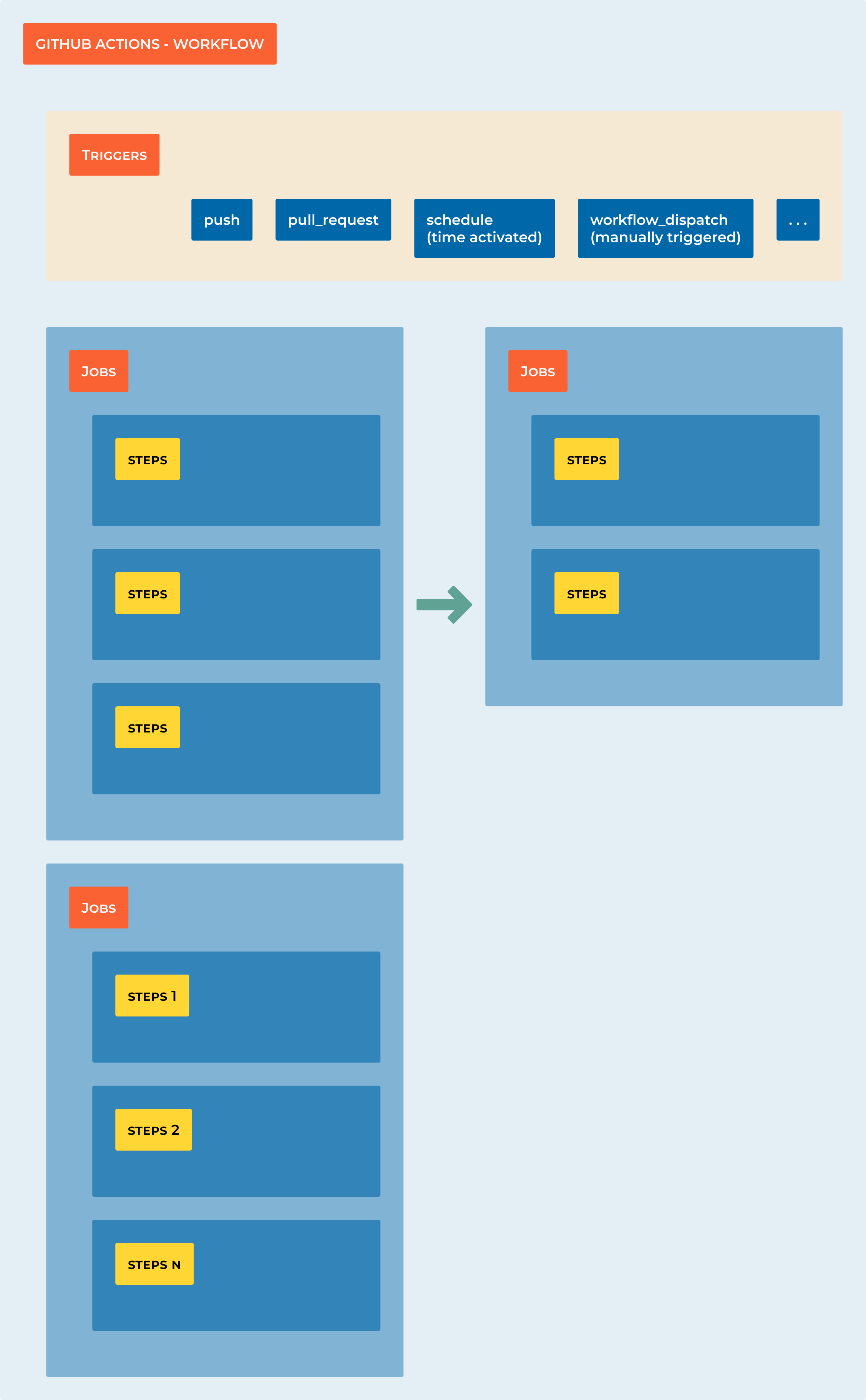
Creating your first workflow
Create a
.github/workflowsdirectory in your repository on GitHub if this directory does not already exist.In the
.github/workflowsdirectory, create a file namedhello_world.yml.Copy the following YAML contents into the
hello_world.ymlfile:
name: Hello World
run-name: ${{ github.actor }} is testing out GitHub Actions
on:
- push
- workflow_dispatch
jobs:
Explore-GitHub-Actions:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- run: echo "The job was automatically triggered by a ${{ github.event_name }} event."
- run: echo "This job is now running on a ${{ runner.os }} server hosted by GitHub!"
- run: echo "The name of your branch is ${{ github.ref }} and your repository is ${{ github.repository }}."
- name: Check out repository code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- run: echo "The ${{ github.repository }} repository has been cloned to the runner."
- run: echo "The workflow is now ready to test your code on the runner."
- name: List files in the repository
run: |
ls ${{ github.workspace }}
- run: echo "This job's status is ${{ job.status }}."
Note
More variables can be found in the GitHub Actions context and expression syntax for GitHub Actions.